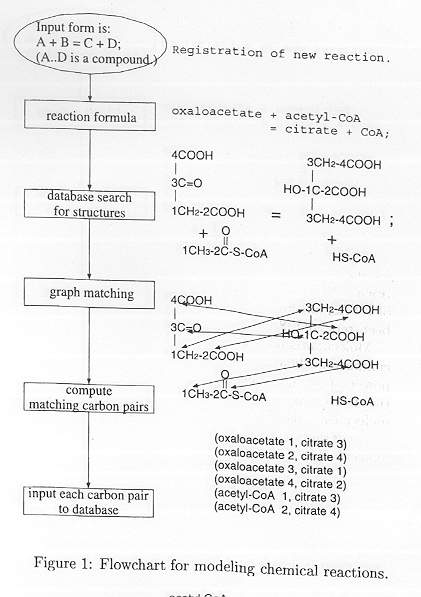
and visit to University of Tokyo, Department of Precision Machinery
History of AROB
Some interesting topics :Impression on U. of Tokyo research activitiesFuture Intelligent Systems DNA computing
Robotic Dog : AIBO in the world cub soccer 2000
| year | #paper | #country |
| 1996 | 72 | 6 |
| 1997 | 38 | 5 |
| 1998 | 186 | 9 |
| 1999 | 206 | 9 |
| 2000 | 240 | 15 |
Large number of participants are Japanese PhD and new faculties.
Intelligent Systems : A system which enhances human intelligence
by the use of science and technology.
Example : internet, mobile phone, manufacturing, transportation, space,
distance learning etc.
Traditional intelligent systems : efficiency for system managers not
for customers.
Future intelligent systems : human friendly, human is customer
not just manager.
Example : electric hybrid vehicles (Honda , 100 km/ 3 litres
)
New meets Old
IMS System AI Brain sci Intelligent Sys
ITS Power sys
ALIFE & Robotics
micro VLSI Quantum
machine Computing
Microtechnology
ME EE CS Material
Intelligent Transport System : Intelligent Highway
60 x 10^12 yen by 2015
Software for this project will be as challenging as internet
VICS (highway), ITC (toll), AHS (smart vehicle)
Internet is an engineering realization of telepathy
Distance learning : shared white board, voice, small no. of students.
TMIT and MIT , 3-4 students do a design project, automatic
parking of a car.
How to encode problem into DNA
Simulation at level of gene
(ATR group)
Model =
the standard DNA model +Features :
context sensitive grammar +
CA with random-chaotic-syntactic parsing/generating +
mRNA-enzyme reaction +
protein verification

molecular computing
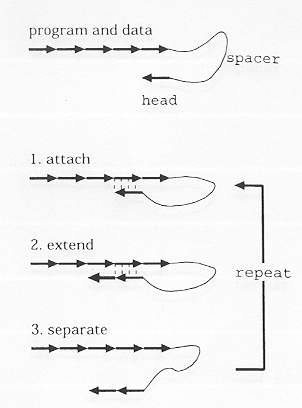
Each DNA consisted of three parts : program, data and head. The
head accesses a particular location in the program (or data), copies one
symbol, and is detached. In the next cycle, the copied symbol becomes
the head, and it will access another location. The flapping movement
is regulated by the reaction temperature, and the termination after copying
is skillfully implemented in the DNA sequence.
(from : Arita, M., "Bio-computing in the 21th century", Proc. of the
5th Int. Symp. on Aritificial Life and Robotics, Oita, Japan, 2000, pp.737-740).